Apr 2025
Journal of American Statistical Association
Forthcoming
Most work on treatment choice and policy learning focuses on utilitarian welfare (i.e., average welfare), which can be sensitive to skewed heterogeneity. We propose a robust policy learning framework that enables the policymaker to act with prudence/negligence and to be influenced by vote shares.
A Computational Approach to Identification of Treatment Effects for Policy Evaluation︎︎︎
with Shenshen Yang
arxiv︎︎︎ matlab codes︎︎︎
2024
Journal of Econometrics
Vol. 240, 105680
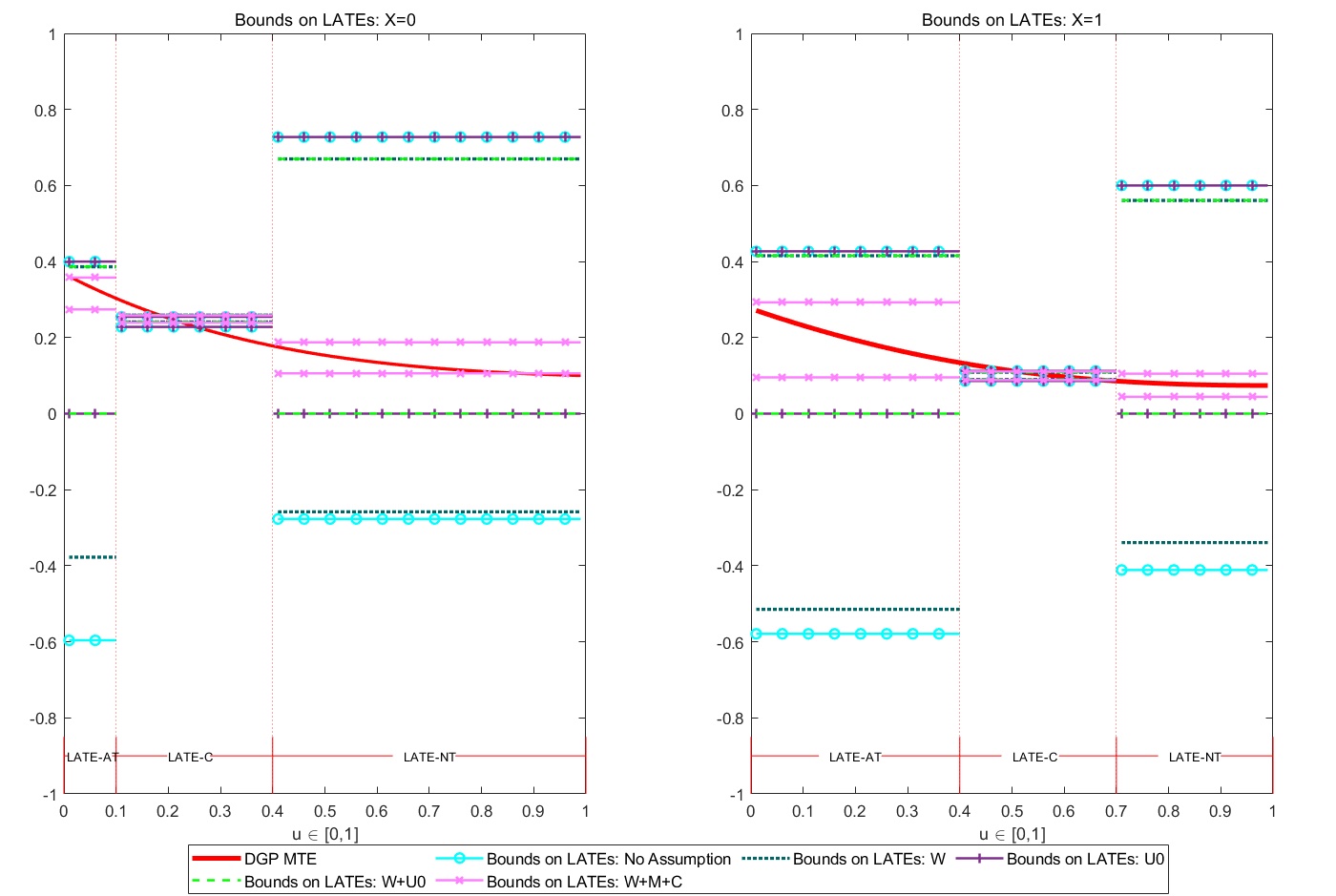
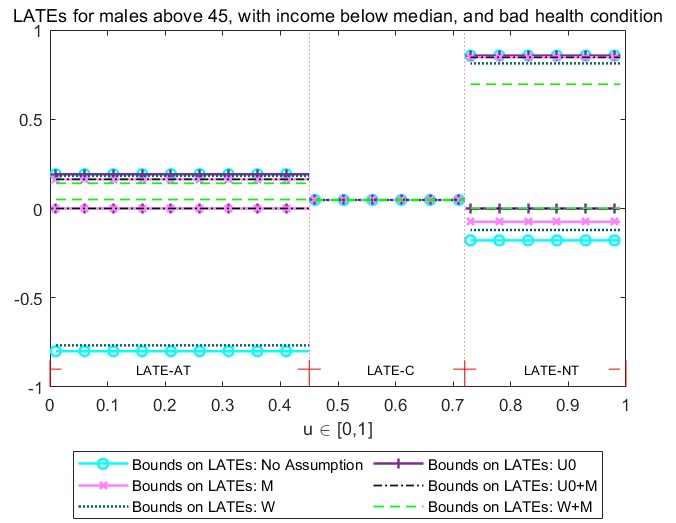
We propose a computational framework to calculate sharp nonparametric bounds (using binary IV that satisfies full independence) on various policy-relevant treatment parameters that are defined as weighted averages of the MTE.
Optimal Dynamic Treatment Regimes and Partial Welfare Ordering︎︎︎
supplement︎︎︎ matlab codes & data︎︎︎ working paper︎︎︎ slides︎︎︎
2023
Journal of American Statistical Association
Vol. 119, pp. 2000-2010
*Editor’s Choice 2023
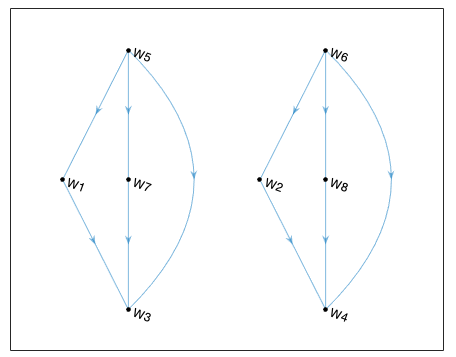
We partially identify the optimal dynamic regime from observational data, relaxing sequential randomization but instead using IVs. As a first step, we establish the sharp partial ordering of welfares, which summarizes the signs of dynamic treatment effects.
2023
Journal of Econometrics
Vol. 234, pp. 732-757
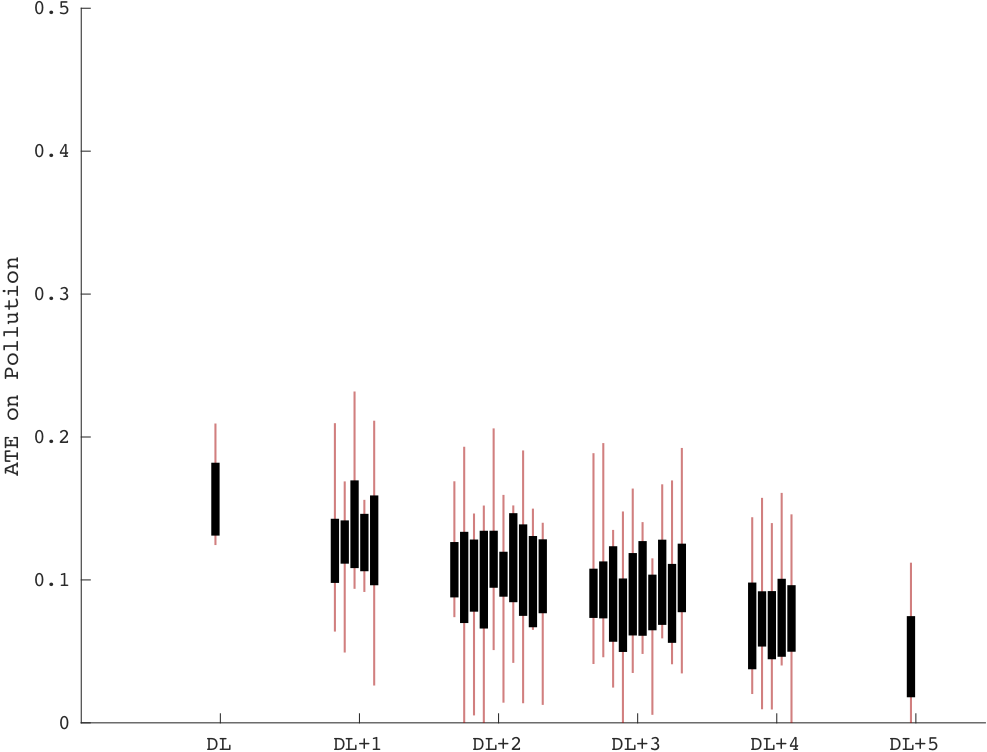
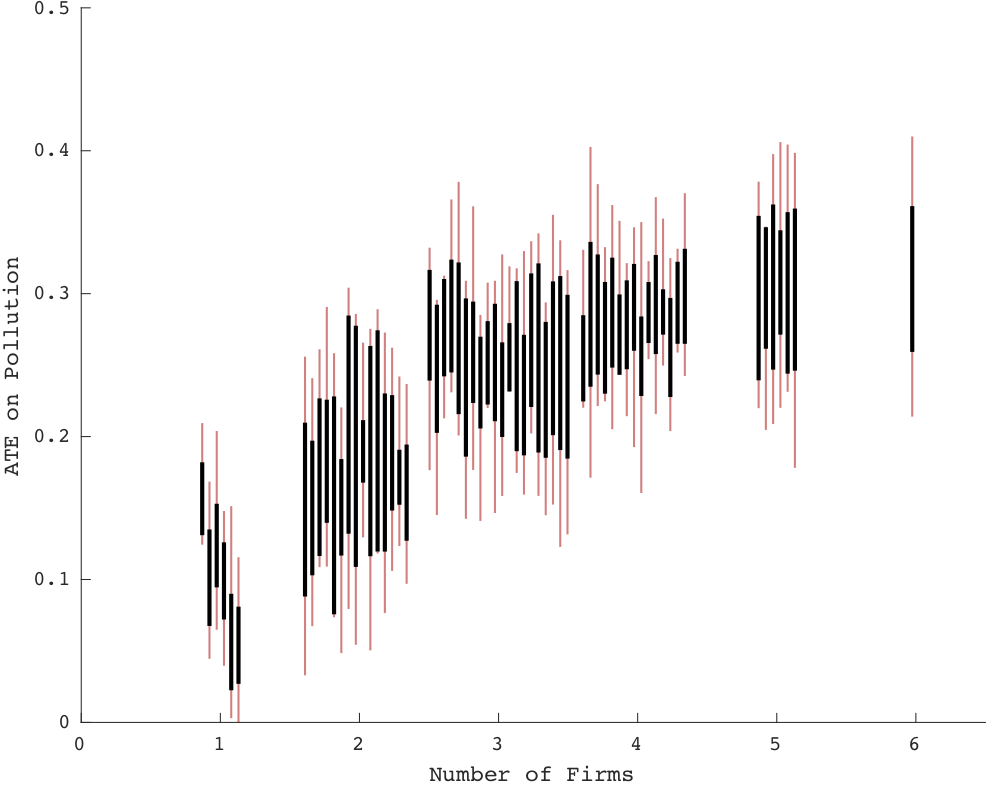
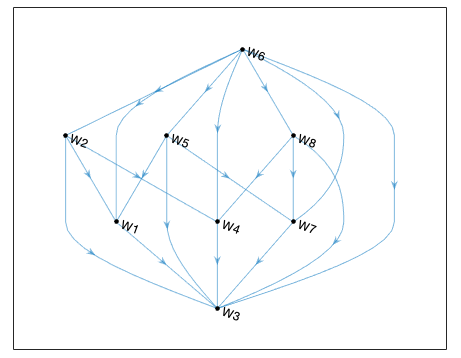
Treatments are determined by strategic interaction, which poses interesting identification problems.
![]()
![]()