Aug 2025
Revise & Resubmit
Journal of Econometrics
Finding IVs is a heuristic and creative process, and justifying exclusion restrictions is largely rhetorical. We propose using large language models (LLMs) to systematically search for new IVs through narratives and counterfactual reasoning.
*This project is featured in the causal inference course at Stanford︎︎︎ and the Lindau Nobel Laureate Meetings 2025︎︎︎.
*This project is featured in the causal inference course at Stanford︎︎︎ and the Lindau Nobel Laureate Meetings 2025︎︎︎.
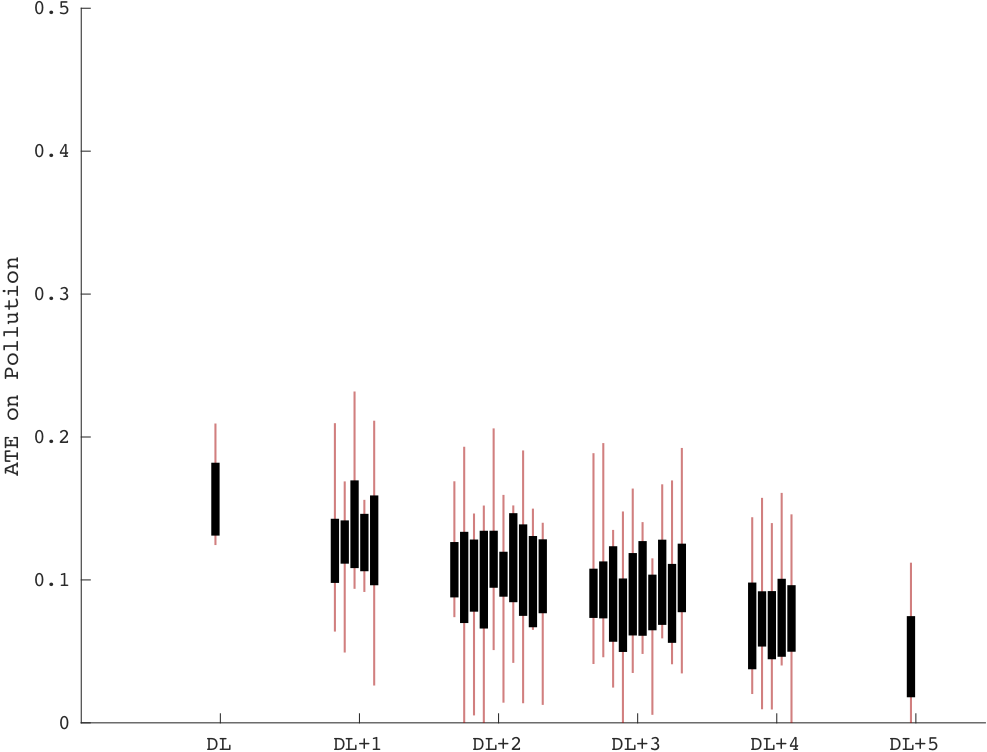
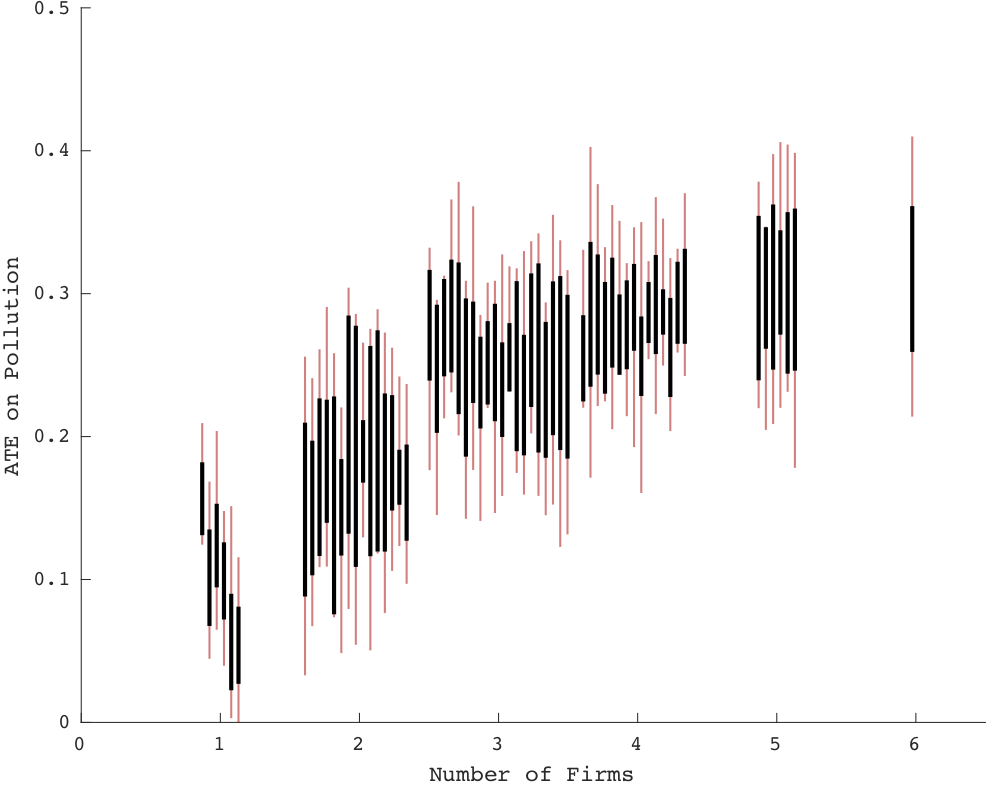
Estimating Causal Effects of Discrete and Continuous Treatments with Binary Instruments︎︎︎
with Victor Chernozhukov, Iván Fernández-Val, Kaspar Wüthrich
arxiv︎︎︎ slides︎︎︎
Dec 2024
Revise & Resubmit
Econometrica
We identify average and quantile treatment effects for binary, ordered and continuous treatments with only binary IV under local copula invariance. The resulting semiparametric estimation procedures are very easy to implement.
Inference for Interval-Identified Parameters Selected from an Estimated Set︎︎︎
with Adam McCloskey
arxiv︎︎︎
Mar 2025
Revise & Resubmit
Quantitative Economics
We develop new inference tools for interval-identified welfare at a policy chosen from an estimated set (e.g., an estimated identified set).
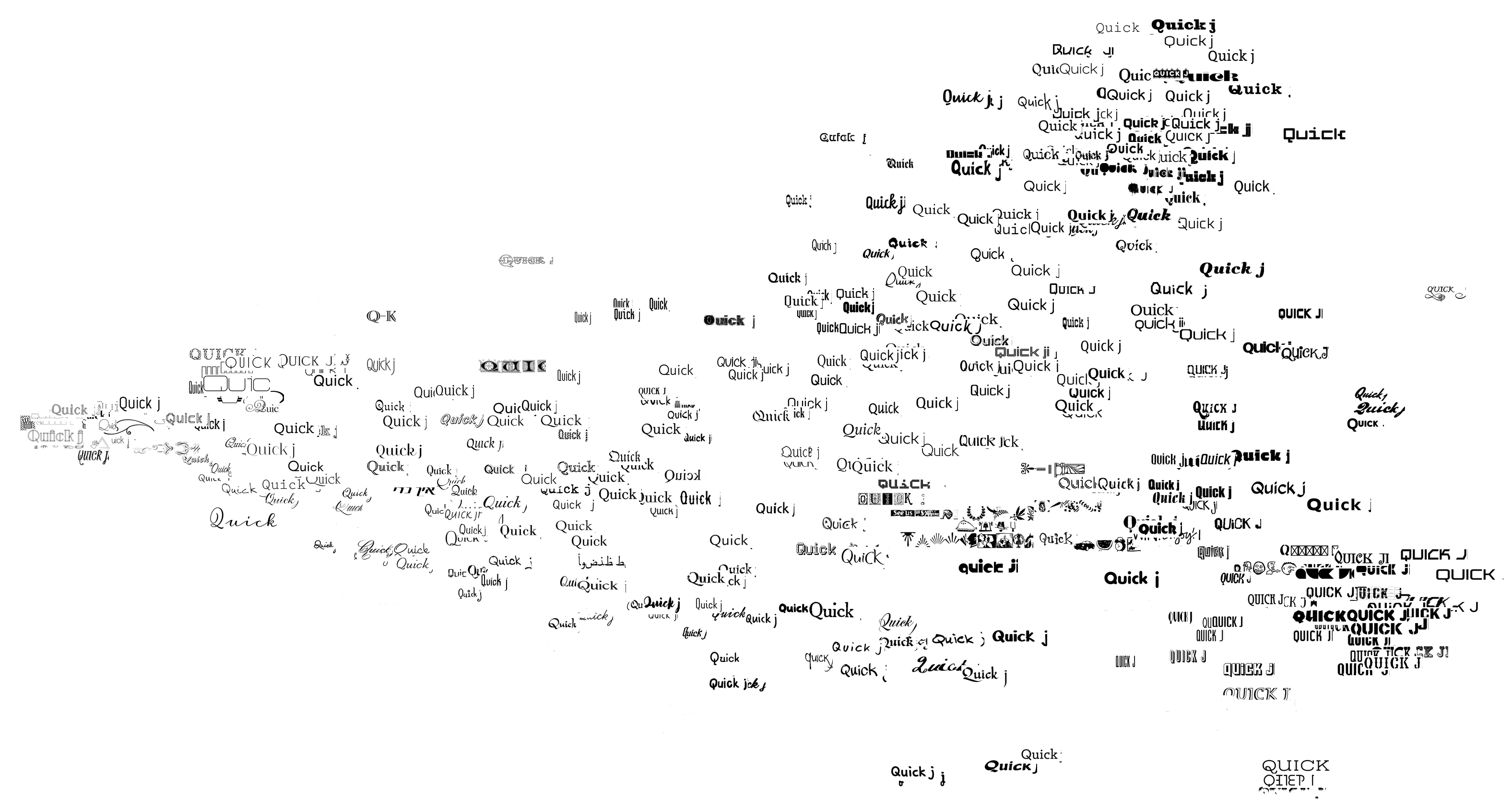
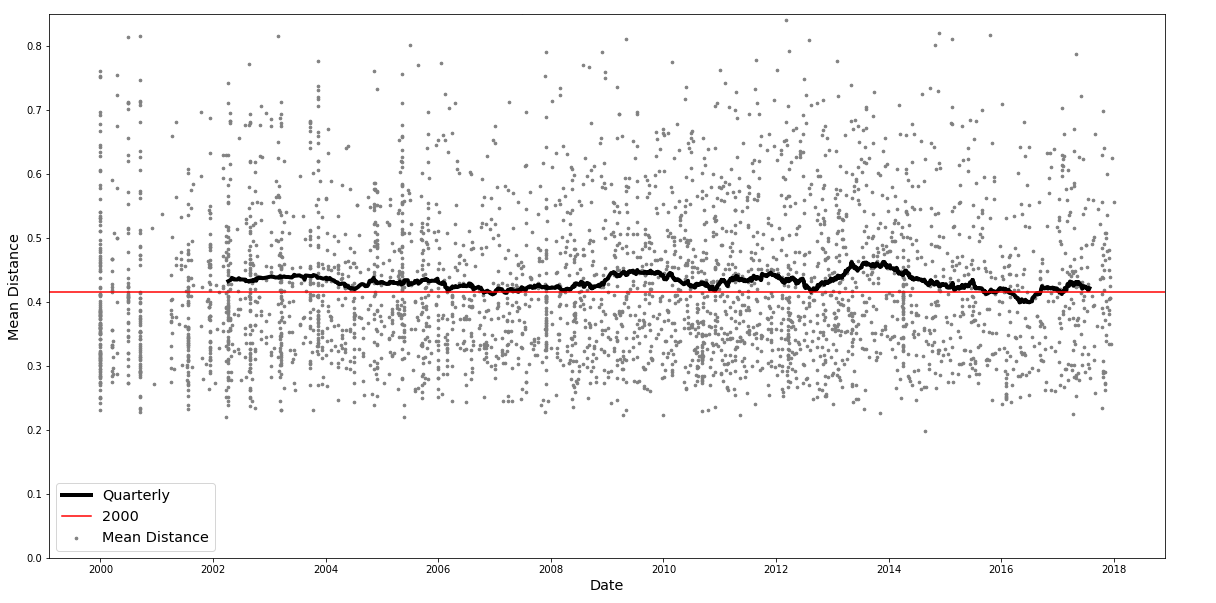
Shapes as Product Differentiation︎︎︎
with Eric Schulman, Kristen Grauman, Santhosh Ramakrishnan
arxiv︎︎︎ slides︎︎︎
Nov 2022
Revise & Resubmit
RAND Journal of Economics
Many differentiated products have key attributes that are high-dimensional (e.g., design, text). We consider one of the simplest design products, fonts, and quantify their shapes by constructing neural network embeddings. Using the embeddings and data from the world's largest online market place for fonts, we study the causal effect of a merger on the merging firm's creative decisions of product differentiation.
*This project is featured in a typography magazine︎︎︎ and included in the MIT graduate machine learning course︎︎︎.

Copyright and Competition: Estimating Supply and Demand with Unstructured Data︎︎︎
with Kyungho Lee
arxiv︎︎︎ ssrn︎︎︎ slides︎︎︎
Sep 2025
Extended abstract at EC’25
To understand the role of copyright policy in the presence of generative AI in markets for products with visual attributes, we estimate a structural model of supply (e.g., product positioning) and demand (e.g., tastes for visual attributes) using image data. Visual similarity, calculated using neural network embeddings, serves as a crucial metric for the analysis.
*Media: KBS Radio 1︎︎︎
*Media: KBS Radio 1︎︎︎
Apr 2025
Journal of American Statistical Association
Forthcoming
Most work on treatment choice and policy learning focuses on utilitarian welfare (i.e., average welfare), which can be sensitive to skewed heterogeneity. We propose a robust policy learning framework that enables the policymaker to act with prudence/negligence and to be influenced by vote shares.
A Computational Approach to Identification of Treatment Effects for Policy Evaluation︎︎︎
with Shenshen Yang
arxiv︎︎︎ matlab codes︎︎︎
2024
Journal of Econometrics
Vol. 240, 105680
We propose a computational framework to calculate sharp nonparametric bounds (using binary IV that satisfies full independence) on various policy-relevant treatment parameters that are defined as weighted averages of the MTE.
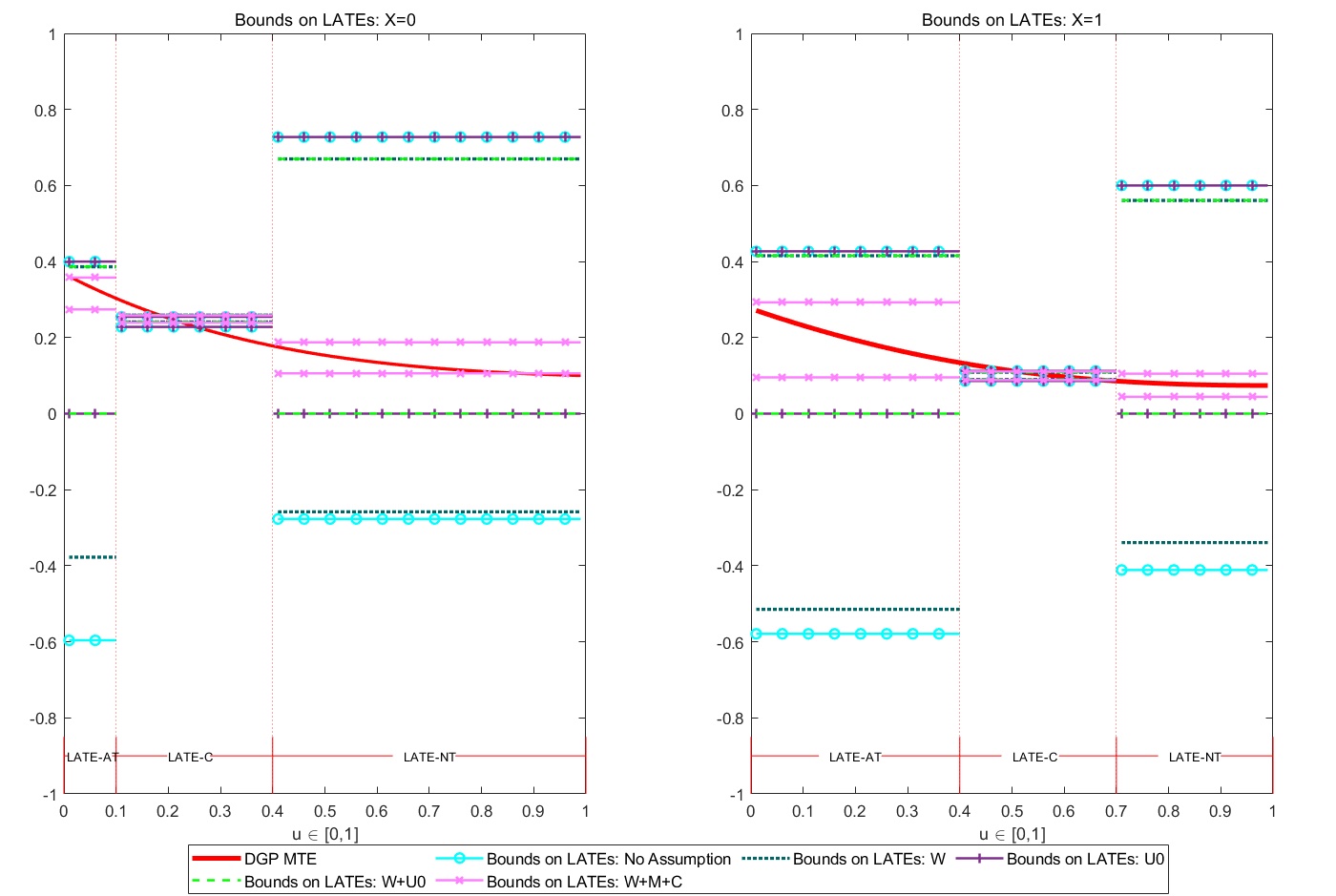
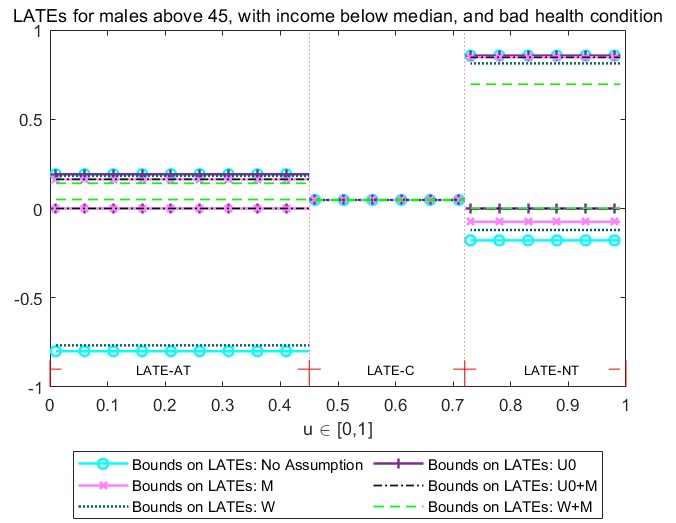
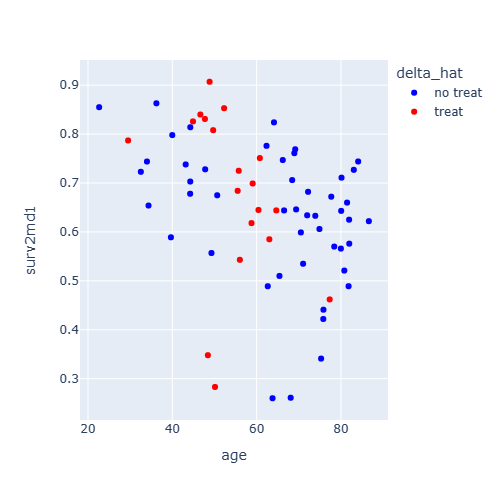
Optimal Dynamic Treatment Regimes and Partial Welfare Ordering︎︎︎
supplement︎︎︎ matlab codes & data︎︎︎ working paper︎︎︎ slides︎︎︎
2023
Journal of American Statistical Association
Vol. 119, pp. 2000-2010
*Editor’s Choice 2023
We partially identify the optimal dynamic regime from observational data, relaxing sequential randomization but instead using IVs. As a first step, we establish the sharp partial ordering of welfares, which summarizes the signs of dynamic treatment effects.
2023
Journal of Econometrics
Vol. 234, pp. 732-757
Treatments are determined by strategic interaction, which poses interesting identification problems.
![]()
![]()